- Two independent channels for device/memory transfers
- Transfer rates up to 40 Mbytes/second
- Configurable System Logic (CSL) peripherals can become bus masters by controlling
a DMA channel
- The DMA channel acts as a "proxy" bus master for the CSL function.
- The CSL peripheral re-uses the bus control logic already embedded in the DMA controller using the
REQSEL and ACKSEL connections on the peripheral's DMA Control register.
- Distributed requests/acknowledge access from within the
CSL matrix
|
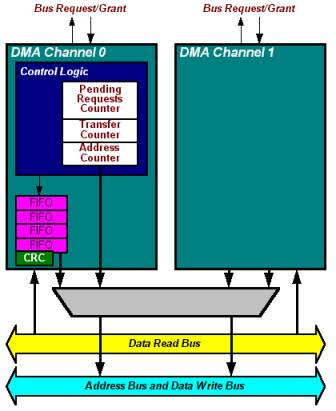
DMA Controller block diagram.
|
